Introduction
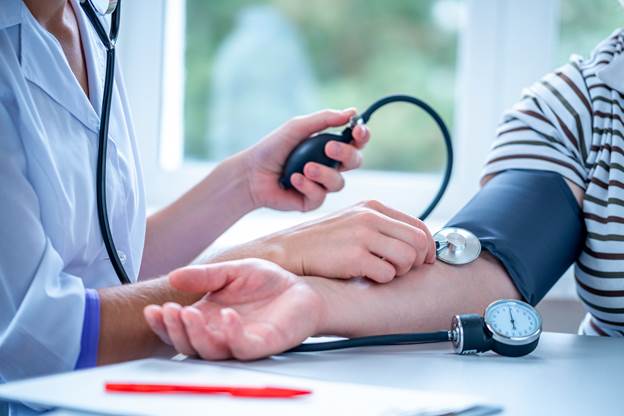
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is one of the most prevalent health conditions worldwide. It is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it usually doesn’t present noticeable symptoms until it leads to more severe health complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, and vision loss.
In this blog, we will explore the causes, symptoms, risks, and effective treatments for hypertension. We will also discuss preventive measures to help control blood pressure and improve overall health.
What is Hypertension?
Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is recorded with two numbers:
- Systolic pressure (the upper number): The pressure in your arteries when your heart beats.
- Diastolic pressure (the lower number): The pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
A normal blood pressure reading is typically around 120/80 mmHg. Hypertension is defined as having consistently high blood pressure readings of 130/80 mmHg or higher.
Causes and Risk Factors for Hypertension
While the exact cause of high blood pressure is often unknown, several factors and conditions may contribute to the development of hypertension:
- Age: The risk of hypertension increases with age, especially after the age of 45 for men and 65 for women.
- Family History: Genetics play a significant role in determining your risk of developing high blood pressure.
- Poor Diet: A diet high in salt, saturated fats, and low in fruits and vegetables can increase blood pressure.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can strain the heart and increase blood pressure.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Physical inactivity contributes to weight gain and can lead to higher blood pressure.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure.
- Smoking: Smoking temporarily raises blood pressure and damages blood vessels, leading to long-term hypertension.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, kidney disease, and sleep apnea can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure.
Symptoms of Hypertension
In most cases, hypertension does not cause noticeable symptoms until it has reached advanced stages. However, some individuals may experience symptoms like:
- Severe headaches
- Shortness of breath
- Nosebleeds
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest pain (in severe cases)
If you experience these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Complications of Hypertension
If left uncontrolled, high blood pressure can cause severe health complications, including:
- Heart Disease: Hypertension is a leading cause of heart attacks, heart failure, and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Stroke: High blood pressure increases the risk of stroke by damaging blood vessels in the brain.
- Kidney Damage: Chronic hypertension can damage the kidneys and lead to kidney disease.
- Vision Loss: High blood pressure can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision impairment.
Managing Hypertension
Managing hypertension involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Here are some ways to control and reduce high blood pressure:
- Healthy Diet:
Adopt a balanced diet, such as the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing sodium and unhealthy fats. - Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, can help lower blood pressure by improving heart health and reducing weight. - Weight Loss:
Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly reduce blood pressure. - Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking:
Reducing alcohol intake and quitting smoking can lower your blood pressure and improve overall heart health. - Stress Management:
Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing, can help manage blood pressure. - Medications:
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough to control blood pressure, doctors may prescribe medications, such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or calcium channel blockers.
Conclusion
Hypertension is a widespread health issue that can lead to severe complications if left untreated. However, with regular monitoring, lifestyle changes, and medications, it is possible to manage high blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other related conditions.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle and making simple changes, you can significantly reduce the impact of hypertension and improve your overall health. Regular check-ups and blood pressure monitoring are essential in preventing and managing hypertension, ensuring a longer, healthier life.
Consult us today at Nexis Multispecialty hospital for expert guidance!